Kick off the smoking habit and regain your bone health!
Radial Club Disease
July 31, 2021
Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis – Occurrence, Treatment & Complications
November 18, 2021Bone health is highly affected by smoking and tobacco consumption through cigarettes, nicotine products such as gum, patches, vape juice, and so on. But it is possible to regain bone health by quitting it as early as possible. With progressing in age, smokers are more likely to experience a host of bone-related diseases and injuries, too. Apart from bones, tissues of the human body also get badly affected.
Research has shown that smoking affects musculoskeletal health such as –
- Restricts the flow of healthy oxygen-rich blood that accelerates the healing process of the bones, muscles, and joints
- Affects the body’s calcium absorption ability leading to weak bones and lower bone density
- The presence of nicotine hampers the production of cells that assist in forming bones and hence the healing process
- Estrogen, an important hormone that builds and maintains healthy bone structure is broken down due to smoking and hence bone health is affected
Research has shown that smoking increases the risk of bone, soft tissues, and disc injuries. Also, the outcome of their treatment and surgeries depends upon the patient’s smoking history. But, smokers are certainly at a high risk of suffering from lung diseases such as COPD, emphysema, cardiovascular diseases, and so on.
Going further, smokers are at a higher risk of getting affected by
Osteoporosis and fractures
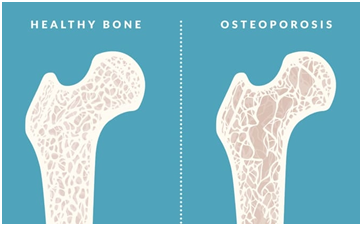
People who smoke could also have poor eating habits, diets, and sedentary lifestyles which lower bone density making them more susceptible to fractures and osteoporosis. They are likely to have hip fractures and/or rotator cuff injuries more than non-smokers especially, senior citizens.
Smokers will take a longer time to recover from bone-related diseases and fractures rather than non-smokers as the presence of nicotine slows down the bone healing process, and their blood flow is restricted.
Osteoarthritis
With research and evidence highlighting the harmful effects of smoking on the bone and cartilage health and also the circulatory system, smokers suffering from osteoarthritis conditions are likely to experience a higher intensity of debilitating pain and ill health.
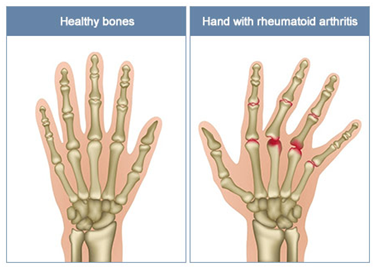
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Smoking increases the risk of systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and other inflammatory autoimmune diseases. Past as well as current smokers are likely to have highly intense symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and joint damage as compared to non-smokers. Quitting tobacco consumption and smoking could reduce the risk of rheumatoid arthritis to a great extent.
Soft Tissue Injuries
Smokers are likely to suffer from sprains, strains, and other trauma-related injuries and also tendonitis, bursitis, or overuse injuries when compared to non-smokers. As mentioned earlier, nicotine in the blood and restricted blood supply slows down the healing process and they take a longer time to recover.
Low back pain/ache
Smoking affects the circulation of the blood and also bone health. Hence, it is possible that the blood flow to the spinal discs is not as required, and they do not receive adequate nutrients which could make smokers susceptible to experience lower backache. Also, the overall health of smokers is compromised due to poor eating habits and limited or no exercise leading to low back pain conditions.
Poor outcomes of surgery
Smoking is known to affect the outcomes of any surgery. So, it is advisable to quit smoking a few weeks or months or totally before any surgery or it takes a toll on ones’ health. Also, smokers complain more about post-surgical pain than non-smokers. They need to consume more medication which has its share of side effects in the long run.
It has been proven that non-smokers have recovered faster and healed better after undergoing elective orthopedic such as knee replacement, spinal fusion, rotator cuff tears as well as trauma injuries such as fractures as compared to patients with smoking history.
Smokers and Sports activities
Exercise and sports are an integral part of staying healthy. But smokers or those people whose lung activity is impaired due to smoking will stay away from playing or even walking. The reason being smoking affects lung growth and the functioning of the lungs as a result less oxygen is available to the muscles for sporting activities.
The performance of smokers is way less than that of non-smokers when compared to their running or walking performance. They experience three times more shortness of breath than non-smokers.
Smoking and a Healthy appetite
Nicotine in cigarettes signals the brain to reduce food intake. A smoker could not be eating healthy foods and getting the adequate nutrition required to stay healthy. A smoker’s immunity and bone health are compromised, and susceptible to fractures and bone injuries which is not a good sign.
Smoking is very harmful to bone and joint health. It affects the blood circulation system and the capacity of bone cell formation. In general, smokers face more risk with bone and trauma injuries while their healing process slows down with not-so-good results as expected in non-smokers.
It is advisable to refrain from smoking or quit smoking as early as possible to ensure healthy bones and body. An active and good physical health is very much essential to living life to the fullest