All you need to know about Cartilage damage in the knee and its repair

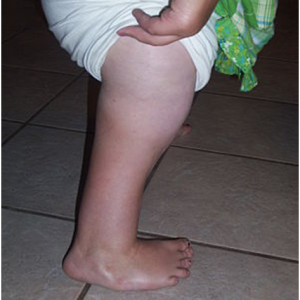
Congenital Femoral Deficiency
April 7, 2022Dr. Ratnav Ratan, a leading orthopedic specialist in Gurgaon and Delhi, shares helpful information on cartilage damage in the knee.
He states, ‘Across my practice as an orthopedic surgeon, any knee pain needs to be checked without any delay. It is vital to prevent further damage to the cartilage as the knees bear most of the body weight when the body is active physically. Further, I would like to add that modern cartilage repair treatment has improved the chances of enjoying better knee health and staying physically active too!’
Cartilage repair in the knee refers to the treatment of damaged cartilage which is a tough yet flexible tissue found in the knee. The cartilage covers the surface of the knee joint, and allows the bones to slide over each other while serving as a shock absorber.
An individual with damaged cartilage in the knee will experience stiffness or swelling accompanied by pain when twisting or rotating the knee. Damage to the cartilage can occur due to sports injury, osteoarthritis which refers to the gradual wear and tear of the joint.
The focus of repair depends upon the extent of cartilage damage in the knee. If the cartilage injury is a minor one, it can recover on its own while in the case of severe cartilage damage, surgical intervention is necessary.
Causes of Cartilage Damage in Children
The most common causes of Cartilage Damage in Children are
- Sudden and/or a traumatic injury from a fall or physical contact
- Wear and tear due to repetitive sports action
Cartilage Damage in Adults
- Osteoarthritis (OA), a degenerative joint disease
- Physical activities such as walking, exercising, and moving can damage the cartilage
- Trauma and/or Injury
Cartilage Damage in Elders
- Oxidative Stress
- Thinning of the cartilage due to decrease in the amount of synovial fluid inside the synovial joints
- Arthritis
- Trauma and/or Injury

Types of cartilage damage in the knees
- Joint Dislocation – The joint gets dislocated from its normal position due to an injury.
- Meniscus Tear – A particular piece of the knee cartilage get injured on account of a forceful twist.
- Impact – Dislocation or tear in the cartilage account of a blow or a fall.
- Inflammation – The patient experiences pain and swelling in the cartilage of the knee
- Infection – The patient suffers from septic arthritis that includes inflammation of the joint.
Treatment options
Conservative options or Non-Surgical options for cartilage repair –
Weight loss and exercise
Weight loss and exercise help in weight reduction which leads to less pressure on the knees on movement. At the same time, strong muscles are capable of absorbing more stress or pressure on the knees when the patient does daily activities or sports. An ideal exercise routine should include leg exercises, cardiovascular exercises, and strengthening exercises. Also, the patient should not feel the pain while cope up with limited bending of the knee.
Bracing
The orthopedic doctor can recommend knee braces which help to relive the weight on the affected side of the knee. These braces are ideal for medial compartmental osteoarthritis that occurs within the knee joint. Moreover, they are customized and hence expensive.
Medicines
The orthopedic doctor can recommend anti-inflammatory medications for reducing the inflammation, swelling and relive the patient from pain. But, it is advisable to consume them for a limited period as they affect the patient’s health if consumed for a long time.
Supplements
Consumption of chondroitin sulfate, glucosamine sulfate and other supplements are recommended as they provide stability to the cartilage.
Hyaluronic acid Injection
Osteoarthritis patients have reduced supply of synovial fluid and hence they face pain and stiffness in joints. An injection of hyaluronic acid directly into the knee joint can help in lubrication of the joints and yield good outcomes.
Cortisone Injection
Cortisone is known for its anti-inflammatory properties, hence it is injected into the knee joint to manage flare-ups. However, repeated use of cortisone damages the articulate cartilage and hence its use should be minimal.
Platelet Rich Plasma Injections
Platelet-rich plasma injections contain growth factors that help in providing symptomatic relief in patients affected with knee osteoarthritis. Also, it protects the cartilage from wear and tear of the knee cartilage in the future. The goal of administration of the PRP injection is to relieve pain and inflammation and improve the knee function with the possibility of avoiding the knee replacement or surgery as recommended by the doctor.
Bone marrow aspirate concentrate (BMAC) Injection
Bone marrow contains adult stem cells which are collected and their concentrated form is injected in the damaged knee joint. In most cases, the marrow present in the hip bone or iliac crest is removed and its aspirate is processed or concentrated in a centrifuge. The final concentrate is rich in growth factors as well as stem cells that promises more relief and management of the damaged knee.
Surgical treatment options for cartilage repair in the knee are –
Microfracture
A microfracture procedure is performed to create a new blood supply for stimulating the growth of new cartilage. Awl, a sharp tool is used to make holes in the subchondral bone which is located below the cartilage. The presence of newly created holes encourages a healing response enabling the blood supply to reach the joint surface along with the new cells and the formation of a new cartilage.
Abrasion Chondroplasty
Abrasion Chondroplasty involves debridement or removal of multiple tissue through a minimally invasive procedure for stimulating growth of new and healthy cartilage. The orthopedic surgeon drills the subchondral bone for initiating a bleeding and healing activity. There is a blood clot formation in the debrided region which develops into a fibrous tissue in place of the worn-out cartilage.
OATS – Mosaicplasty procedure
In this procedure, the bone and cartilage plugs available in the non weight bearing surfaces of the patient’s joints are inserted in the affected knee joint area to stimulate the growth of the cartilage on its surface. This procedure is most preferred for cartilage damage on account of trauma.
OATS refers to Osteochondral Autograft Transfer System while transplanting several cartilage plugs is known as Mosaicplasty.
ACI- Autologous Chondrocyte implantation
Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation (ACI) is a dual step procedure performed on young patients with single defects in larger size than 2 cms. In the ACI procedure, the patient’s own cells are used which reduces the risk of reduction.
In the first step of an ACI procedure, healthy cartilage tissue that contains chondrocytes or healthy cartilage cells is removed from non-weight bearing area of the bone through an arthroscopic procedure. These cells are cultured in a laboratory and their number increases considerably in 3 to 5 weeks.
The second step involves an arthrotomy, an open surgical procedure to implant the newly grown cells in a specially prepared cartilage defect area within the knee joint.
Biocartilage Arthrex

Biocartilage Arthrex refers to a cartilage autograft implantation system (CAIS) in which minced cartilage is used to fill defects. The procedure involves using minced pieces of cartilage supported over a scaffold or glued with together with a fibrin adhesive layer. This helps even distribution of chrondrocytes for expansion within the defect while offering mechanical as well as structural protection. Also, the use of minced cartilage technique minimizes the need for donor tissue required for the repair.
Osteochondral Allografts
Osteochondral Allografts refer to the tissue received from a donor. The orthopedic surgeon performs an osteochondral grafting procedure to treat cartilage injuries in which the underlying bone is exposed. The goal of osteochondral grafting is to replace the cartilage on the affected bone and its surface too. Osteochondral Allografts are used to repair cartilage damage in the knee joints.
Bone Osteotomy combined to correct limb alignment
Cartilage damage can lead to issues in straightening the lower limbs especially the knees. The orthopedic surgeon performs a knee osteotomy to cut and reshape the upper shinbone (tibia) or the lower thighbone (femur). The goal of the knee osteotomy is to reduce the pressure on the damaged side of the knee joint.