Spastic Cerebral Palsy – How Botox Injections Can Help Your Child?
Platelet-Rich-Plasma (PRP) Therapy for Joint Pain
September 28, 2020
Knock Knees- Everything you need to know
October 16, 2020
A cerebral palsy is a group of disorders that affects movement, balance and posture of the body. It happens due to abnormal brain development or damage to a developing brain. It affects the brain’s ability to control muscles.
The symptoms of the disorder of cerebral palsy differ from person-to-person, these symptoms include:
- Intellectual disability
- Seizures
- Problems with vision
- Hearing or speech problems
- Joint problems or changes in the spine
According to Dr. Ratnav Ratan, an experienced pediatric orthopedic doctor in Gurgaon, the most common type of cerebral palsy is spasticity. And yes, it does exist in children as well.
Spastic cerebral palsy happens because of an injury in the bundles of neurons in your child’s brain and spinal cord. Because of this, your child might find it challenging to move from one position to another. Also, they might find it hard to control their muscles to perform regular tasks like sitting, walking, feeding, holding objects or speaking. You might even notice that their movements seem jerky.
Your child will be severely hampered by this condition, to the point where they feel pain, have disturbed sleep and many other problems. However, we have a solution for your child’s pain and suffering.
The most widely suggested treatments for spastic cerebral palsy in children less than 7 years is the use of Botulinum toxin type A (Botox) injections into the affected muscles. These injections can also benefit other causes of spasticity like traumatic brain injury, stroke, multiple sclerosis and spinal cord injury.
How do Botox Injections Work?
Your doctor will begin by thoroughly examining some crucial factors like:
- Affected muscles of your child
- Track his/her development
- Your child’s IQ
- Presence of abnormal body movements (if treatment is suitable or not)
However, your child cannot receive the treatment under some circumstances, which include:
- If your child has a fever, cold or flu-like symptoms.
- If your child has received vaccinations (a week before treatment)
- Your child is about to get vaccinated within 7 days after Botox treatment
Why use Botox for Spastic Cerebral Palsy?
Botox injections, when used for spastic cerebral palsy, has shown several benefits, such as
- Preventing joint contractures
- Improvement in positioning and range of motion
- A decrease in muscle stiffness
- Improved mobility
- Increased ease of care (diaper care, feeding, bathing etc.)
Botox relaxes the muscles by blocking the brain impulses asking it to contract. It temporarily reduces unwanted muscle tightness in a child with severe cerebral palsy, improving their comfort and movement.
This method is even more effective when used in conjunction with occupational therapy. After Botox injections, it becomes easier for parents and therapist to help the child become comfortable while sleeping on bed and sitting.
How does Botox work for Spastic Cerebral Palsy?
Many companies manufacture Botulinum toxin-A (Botox). The common trade names include BOTOX® and Dysport®. It comes as vacuum dried crystals in vials which require dilution before use.
Botox, when injected into the muscle belly, it impairs the release of a neurotransmitter called Acetylcholine. This contracts the skeletal muscles of the human body at the neuromuscular junction making the muscles temporarily weaker. It is also effective on the gastrocnemius-soleus complex, hamstrings, hip flexors, adductors and flexor synergy muscles of the upper extremity.
Your paediatric orthopaedic doctor will follow the procedure in a succession of stages as mentioned below:
Stage 1: Before the treatment
You doctor will consider several factors before the treatment to calculate the dosage your child requires, such as:
- Age
- Bodyweight
- Muscle size
- Location of muscle
- Degree of spasticity
Stage 2: During the treatment
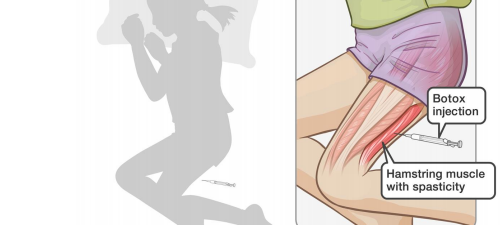
The doctor will follow these steps:
- Before giving the Botox injections, the doctor will first identify the tight muscle groups that need to be injected. Your child will receive general anesthesia
- The limb is prepped and draped. The injection is administered using a small needle on a special syringe using joint movements, ultrasound guidance or nerve stimulator to locate the exact muscle belly.
- The number of injections will depend on your child’s weight, the size of the muscle and their number.
- Botox muscle injections can take from 60 to 90 minutes, depending on the number of muscles that require the injections.
Stage 3: After the treatment
Most children will go home within a few hours of receiving the Botox injections. After the Botox, the child may continue doing daily activities.
Your pediatric orthopaedic surgeon might prefer plastering the limbs to help stretch the muscles for about 6-12 weeks. You will notice muscle relaxation after about 48 to 72 hours of the treatment, and it continues for around 6-8 months.
After cast removal, your doctor will give splints to your child for maintaining the corrected position of the joints and maintain the stretch while walking and sleeping.
Your therapists will work on strengthening of muscle on the opposite side of the affected joint. It provides nursing care and improves the walking ability of the child.
After 6 months, the effects of the treatment will wear off, so, your child might face muscle tightness again. In such a case, your doctor might suggest re-injection of Botox.
Remember, Botox is one part of a multidisciplinary treatment program in cerebral palsy. You should ensure regular follow-ups for your child to best observe the benefits of the procedure and provide treatment for your child as and when required.
What are the risks of Botox?
Even though Botox treatment is safe, there is a small possibility that unexpected or unusual reactions to Botox may occur. These reactions may even take place in areas of your child’s body that received no injections.
The most common side effects are:
- Fever
- Malaise
- Muscle soreness
- Pain, redness or swelling at the injected area
- Infection in the injected area
Your child requires immediate medical care if they experience any of the following symptoms:
- Severe weakness
- Speech has become more difficult to understand, or voice changes (e.g., hoarse voice)
- Difficulty breathing
- Drooping eyelids or changes in vision
- Allergic reaction (anaphylaxis)
Your child might not get a permanent solution to cerebral palsy from Botox. However, studies have shown that it helps in reducing upper limb spasticity and in improving movement pattern, gait and fine motor function of children with spastic cerebral palsy. The effect of this treatment generally lasts for around 6-8 months and may be repeated.