How to treat meniscal tear in children & prevent them?
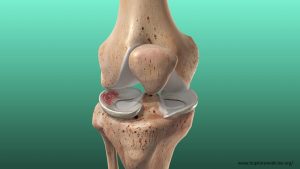
Knees of children and teenagers, especially those who play active sports such as hockey, volleyball, football, and soccer, are likely to experience structural injuries. It is essential to know that knees have shock-absorbing cartilage called the meniscus, which can tear, causing considerable pain and discomfort.
A sudden twisting motion in the knee along with a pop sound indicates that there could be a meniscus tear. The patient finds it difficult to bend and straighten the knee. At times, the knee gets stuck up or locked too. This condition is painful as the meniscus is a shock absorber between the shinbone and the thigh bone.
Diagnosis and Clinical presentation of meniscal tear.
The doctor examining the meniscus tear will try to bend or straighten the injured knee from below, at which the patient will experience pain and discomfort. The patient will also experience tenderness along the thigh, leg, and/or shin bones.
The doctor will examine the affected and the unaffected leg to compare and infer the extent of injury and damage. The series of examinations include inspections, range of motion, palpation, tests to determine the integrity of the menisci, the knee joint, and its structures.
Imaging tests for Diagnosis
x-rays – Though not very useful, x-rays are recommended to rule out other knee issues that show similar symptoms.
MRI – MRI is considered to be one of the best imaging tests to detect a meniscus tear. The MRI provides highly detailed images of hard and soN tissues within the knee for further diagnosis.
Treatment of meniscus tear
The location of the meniscus tear and the vascularity also determines the type of treatment.
An unrepairable tear in the meniscus implies loss of functionality of the meniscus, which absorbs shocks and helps the knee function smoothly.
- I.C.E. Treatment – Low-grade meniscus tear is treated through rest, icing, elevation and bandaging or the use of compression sleeves to prevent and control the swelling. It is essential to avoid putting weight on the injured knee.
- Smaller, asymptomatic tears does not require Patients do well with supervised knee strengthening exercises and lifestyle modifications. Avoidance of squatting and cross leg sitting helps most patients avoid surgery.
- Surgical Treatment is considered for symptomatic tears where the patient fails to respond tp conservative treatment. Technique depends on these factors –
- Location of the tear
- Age of the patient
- Self healing quotient of the tear
-
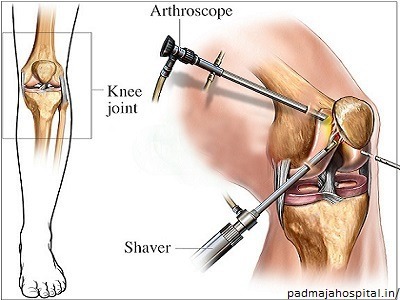
Meniscus Repair using Arthroscopy(Key hole surgery)
The absence of blood supply in the meniscus implies longer periods of healing and recovery. It is advisable to perform repair procedures in the peripheral meniscal region with a blood supply in the outer third portion of the meniscus. Tears of size one cm or more in length are unlikely to heal on their own. Therefore, it becomes essential to repair the torn tissue and accelerate the self-healing process to enable the patient to resume routine and active sports sooner. The ‘All-Inside’ meniscus repair is done through an arthroscope. We employ special suturing techniques to repair the tear without giving big incisions The suture knots are tied internally
-
Arthroscopic meniscectomy/Trimming +Balancing
This is an outpatient minimally invasive surgical procedure performed to resolve a torn meniscus cartilage in the knee. In most cases, we removes the torn part of the meniscus, balance the meniscus followed by physical therapy. It could take nearly 4- 6 weeks post arthroscopy for full recovery.
A word of caution
Considering the patient is a growing individual who has not yet attained full bone growth, it is advisable to seek an experienced pediatric orthopedist to perform the arthroscopic surgery in children. The number of incisions, the size of incisions, and the repair location are some of the important decisive factors on which the success of the arthroscopy depends.
The surgeon should have experience performing meniscus repair surgeries on children as they have pristine cartilage surfaces and relatively small joint spaces.
Lastly, valuable tips to prevent a meniscus tear are
- Never ignore knee pain – The pain and discomfort increase gradually, causing grave damage to the knee
- Dynamic stretching is a must
Young children, as well as athletes, should always warm up their leg muscles before as well aNer exercise or playing sports. Dynamic stretching helps in not only preventing injuries but also reducing muscle soreness aNer games or training. - Ensure good muscle strength of lower limbs
- Leg muscles
Young children and athletes need to strengthen their leg muscles as they decrease the pressure on the joint and reduce the amount of weight that the meniscus in your knees needs to absorb. In addition, they should concentrate on strengthening their quadriceps, hamstrings, abductors, and adductors muscles. - Hip and buttocks muscles
Yes, they are equally important with regards to knee stability. The hip joint connects the upper body with the legs. Therefore, it is essential to have strong and balanced hip joints as they help in proper alignment and movement of knees without twisting.
- Leg muscles
- Rest
Ample and adequate rest is necessary aNer exercise and play. Muscles develop microtears which can deteriorate further, leading to inflammation. Inflamed muscles mean a higher risk of grave injuries