If yes, make sure you consult Dr. Ratnav Ratan, a leading sports injuries doctor in Gurgaon, regarding your knee health.
Dr. Ratnav Ratan is the an experienced orthopedic doctor in Gurgaon who will conduct a physical examination of the knee and discuss the symptoms with the patient. He will check for swelling, stiffness, tenderness, and even issues when moving the knees. He may suggest MRI scan along with x-rays to assess the damage in the muscles, tendons, and cartilage. This will help the surgeon to decide the future line of treatment.
Knee cartilage injury is treated through non-surgical as well as surgical treatment.
In the initial stages of knee cartilage treatment, the orthopedic doctor will emphasize the non-surgical approach – R.I.C.E treatment –
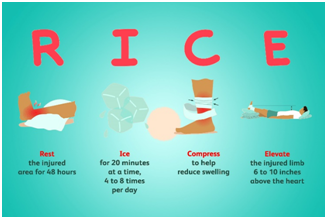
The surgeon may suggest an intake of painkillers to reduce inflammation and swelling along with physical therapy.
Surgery: There are several surgery options available to repair knee cartilage injuries. However, the orthopedic surgeon will recommend which surgery will prove suitable to resolve the knee cartilage issue.
The cartilage tissue does not contain blood vessels and hence unable to heal on its own. Thus, the orthopedic surgeon recommends surgery and make tiny cuts or abrasion in the bone below the injured cartilage to induce bleeding required to grow new cartilage cells.
Dr, Ratnav Ratan, a leading Trauma & Injuries Doctor in Gurgaon is available for consultation for treatment and diagnosis of knee cartilage injuries.
The surgery focuses on removing the damaged cartilage as much as possible. The surgeon will use a scraping tool to remove the damaged cartilage and roughen the affected bone’s surface.
The surgeon will use a wire or a drill or wire and make tiny holes in the bone. The nearby tissue will be injured, leading to problems along with bone cysts for the required healing.
The surgeon will use an awl to pierce the bone after clearing the damaged cartilage.
The treating orthopedic surgeon will decide the type of knee cartilage replacement procedure suitable for the patient. The size of the cartilage area and the patient’s health condition determines the type of cartilage repair surgery.
Surgeons can perform osteochondral autograft transplantation or osteochondral allograft transplantation surgeries, which are done through an arthroscope.
These surgeries involve grafting healthy cartilage either from the patient or from a cadaver and placing them in the area requiring new cartilage. The surgeon may perform a mosaicplasty wherein multiple grafts are involved.
It is a surgery in which the surgeon removes a small piece of healthy cartilage from the knee joint. This piece of cartilage is then cultured for new cell growth. After a gap of 3 – 5 weeks, the new cartilage cells are implanted into the damaged knee joint. The second surgery is an open surgery and requires a larger incision.
Autologous chondrocyte implantation is recommended in case of repair of relatively large-sized multiple cartilage injuries.


Chondromalacia patella refers to the wear and tear of the cartilage below the underside of the knee cap. The cartilage located at the underside of the knee cap will be soft, cracked, and even broken down, and the patient will complain of severe knee pain in the front area of the knee. It occurs more in women because of the lower leg alignment.
However, the patient will complain of pain related to chondromalacia due to frequent use of stairs, rising from a seated position and when sitting in a position with bent knees for long periods.
The non-surgical approach to managing the chondromalacia of patella includes consuming anti-inflammatory medicines and avoiding activities that increase the pain and discomfort.
The orthopedic surgeon will suggest not to indulge in activities such as using an elliptical trainer or a Stairmaster or playing volleyball, basketball etc that cause further strain on the kneecap. The surgeon may also advise rest if the kneecap is misaligned since early childhood.
Chondroplasty or arthroscopic shaving or Knee debridement is the most preferred way to treat the chondromalacia of the patella condition in the patient.
In this surgery, the surgeon will access the patella using an arthroscope to shave off the roughness on the underside of the patella and perform a lateral retinacular release.
A lateral retinacular release means the surgeon will loosen up the extra pressure of the knee cap against the thigh bone and rectify the kneecap’s alignment.
Patellofemoral replacement is another major surgery recommended in the event of an unsuccessful result of Chondroplasty.
Act in time and seek an appointment of Orthopedist Dr. Ratnav Ratan, for treatment of knee cartilage injuries and related issues and prevent any further damage to the knees.

https://wa.me/919868639352?text=Hello%20Dr%20Ratnav,%20I%20want%20to%20book%20a%20video%20consultation%20for%20my%20child.